Projects
One-Line-of-Code Data Mollification Improves Optimization of Likelihood-based Generative Models
Abstract
Generative Models (GMs) have attracted considerable attention due to their tremendous success in various domains, such as computer vision where they are capable to generate impressive realistic-looking images. Likelihood-based GMs are attractive due to the possibility to generate new data by a single model evaluation. However, they typically achieve lower sample quality compared to state-of-the-art score-based diffusion models (DMs). This paper provides a significant step in the direction of addressing this limitation. The idea is to borrow one of the strengths of score-based DMs, which is the ability to perform accurate density estimation in low-density regions and to address manifold overfitting by means of data mollification. We connect data mollification through the addition of Gaussian noise to Gaussian homotopy, which is a well-known technique to improve optimization. Data mollification can be implemented by adding one line of code in the optimization loop, and we demonstrate that this provides a boost in generation quality of likelihood-based GMs, without computational overheads. We report results on image data sets with popular likelihood-based GMs, including variants of variational autoencoders and normalizing flows, showing large improvements in FID score.
Publications
Tran, Ba-Hien; Franzese, Giulio; Michiardi, Pietro; Filippone, Maurizio. One-Line-of-Code Data Mollification Improves Optimization of Likelihood-based Generative Models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2023 (to appear).
Tran, Ba-Hien; Franzese, Giulio; Michiardi, Pietro; Filippone, Maurizio. Improving Training of Likelihood-based Generative Models with Gaussian Homotopy. ICML Workshop on Structured Probabilistic Inference and Generative Modeling, 2023.
Fully Bayesian Autoencoders with Latent Sparse Gaussian Processes
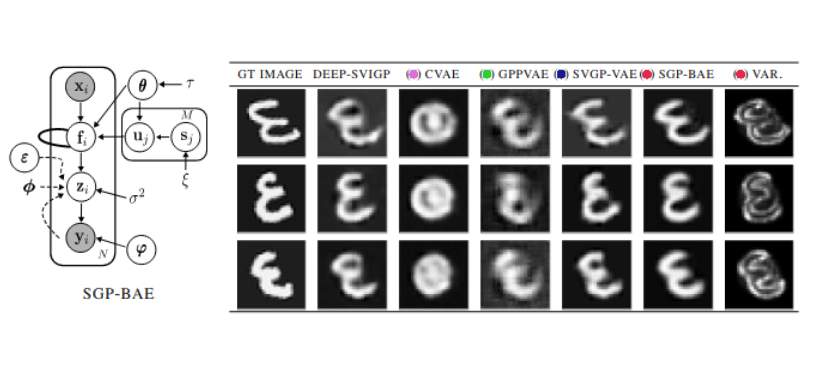
Abstract
Autoencoders and their variants are among the most widely used models in representation learning and generative modeling. However, autoencoder-based models usually assume that the learned representations are i.i.d. and fail to capture the correlations between the data samples. To address this issue, we propose a novel Sparse Gaussian Process Bayesian Autoencoder (SGPBAE) model in which we impose fully Bayesian sparse Gaussian Process priors on the latent space of a Bayesian Autoencoder. We perform posterior estimation for this model via stochastic gradient Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. We evaluate our approach qualitatively and quantitatively on a wide range of representation learning and generative modeling tasks and show that our approach consistently outperforms multiple alternatives relying on Variational Autoencoders.
Publications
Tran, Ba-Hien; Shahbaba, Babak; Mandt, Stephan; Filippone, Maurizio. Model Selection for Bayesian Autoencoders. International Conference on Machine Learning, 2023.
Model Selection for Bayesian Autoencoders
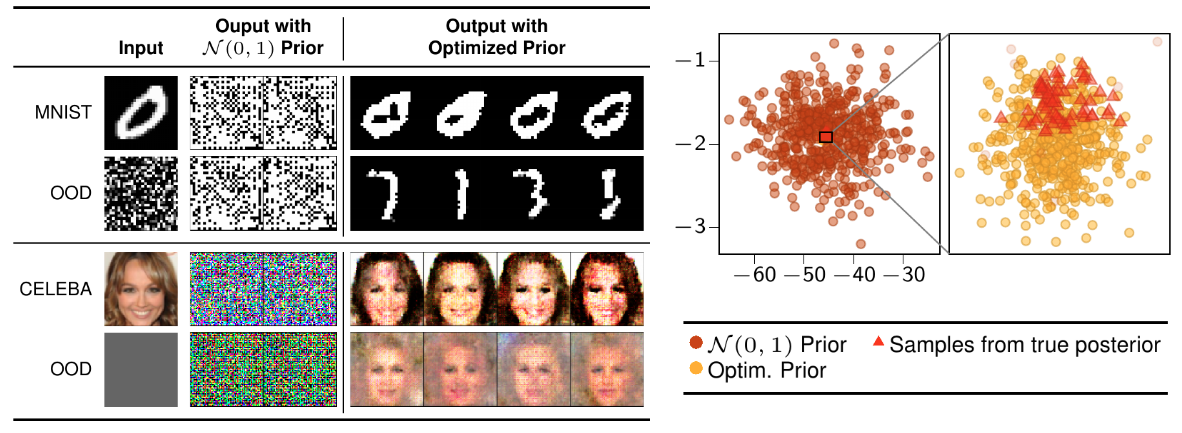
Abstract
We develop a novel method for carrying out model selection for Bayesian autoencoders (BAEs) by means of prior hyper-parameter optimization. Inspired by the common practice of type-II maximum likelihood optimization and its equivalence to Kullback-Leibler divergence minimization, we propose to optimize the distributional sliced-Wasserstein distance (DSWD) between the output of the autoencoder and the empirical data distribution. The advantages of this formulation are that we can estimate the DSWD based on samples and handle high-dimensional problems. We carry out posterior estimation of the BAE parameters via stochastic gradient Hamiltonian Monte Carlo and turn our BAE into a generative model by fitting a flexible Dirichlet mixture model in the latent space. Consequently, we obtain a powerful alternative to variational autoencoders, which are the preferred choice in modern applications of autoencoders for representation learning with uncertainty. We evaluate our approach qualitatively and quantitatively using a vast experimental campaign on a number of unsupervised learning tasks and show that, in smalldata regimes where priors matter, our approach provides state-of-the-art results, outperforming multiple competitive baselines.
Publications
Tran, Ba-Hien; Rossi, Simone; Milios, Dimitrios; Michiardi, Pietro; V. Bonilla, Edwin; Filippone, Maurizio. Model Selection for Bayesian Autoencoders. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021.
Functional Priors for Bayesian Neural Networks
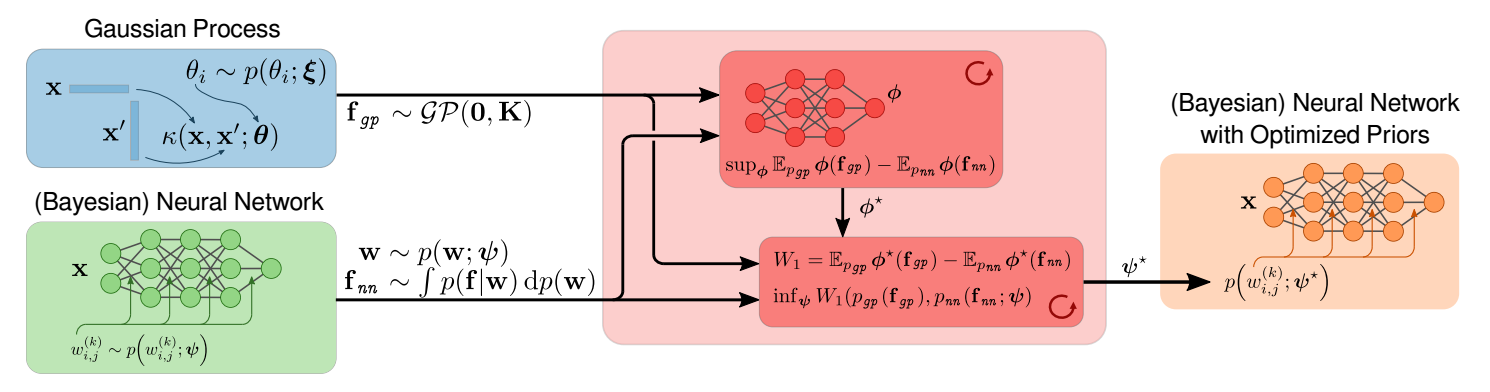
Abstract
The Bayesian treatment of neural networks dictates that a prior distribution is specified over their weight and bias parameters. This poses a challenge because modern neural networks are characterized by a large number of parameters, and the choice of these priors has an uncontrolled effect on the induced functional prior, which is the distribution of the functions obtained by sampling the parameters from their prior distribution. We argue that this is a hugely limiting aspect of Bayesian deep learning, and this work tackles this limitation in a practical and effective way. Our proposal is to reason in terms of functional priors, which are easier to elicit, and to “tune” the priors of neural network parameters in a way that they reflect such functional priors. Gaussian processes offer a rigorous framework to define prior distributions over functions, and we propose a novel and robust framework to match their prior with the functional prior of neural networks based on the minimization of their Wasserstein distance. We provide vast experimental evidence that coupling these priors with scalable Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling offers systematically large performance improvements over alternative choices of priors and state-of-the-art approximate Bayesian deep learning approaches. We consider this work a considerable step in the direction of making the long-standing challenge of carrying out a fully Bayesian treatment of neural networks, including convolutional neural networks, a concrete possibility.
Publications
Tran, Ba-Hien; Rossi, Simone; Milios, Dimitrios; Filippone, Maurizio. All You Need is a Good Functional Prior for Bayesian Deep Learning. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2022.
Tran, Ba-Hien; Milios, Dimitrios; Rossi, Simone; Filippone, Maurizio. Functional Priors for Bayesian Neural Networks through Wasserstein Distance Minimization to Gaussian Processes. 3rd Symposium on Advances in Approximate Bayesian Inference, 2021.
